雷射準直鏡
Brand: iAPhotonics
The laser diode collimators, or laser diode collimating lens, are optical elements which focus the laser beams, or just focus at infinity with little or no parallax. For different uses, they are desig..
樣品價格 NT$297
Brand: iAPhotonics
The laser collimating lens, or collimator lens, are optical elements which focus or de-focus the laser beams, or just focus at infinity with little or no parallax. For different uses, They are designe..
樣品價格 NT$396
Brand: iAPhotonics
The laser collimator, or collimator lens, are optical elements which focus or de-focus the laser beams, or just focus at infinity with little or no parallax. For different uses, They are designed in d..
樣品價格 NT$660
顯示 1 - 4 / 4 (共 1 頁)











































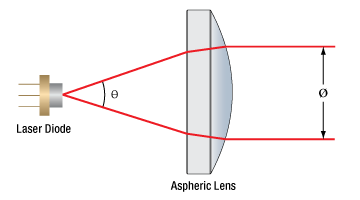 視準透鏡、雷射準直鏡、雷射二極體準直鏡、雷射準直儀
視準透鏡、雷射準直鏡、雷射二極體準直鏡、雷射準直儀


