影像模組 - 產品資訊
Camera
Sensor Module Guideline
Camera Sensor Module Guideline
introduces IADIY's image sensor modules, camera sensor modules and USB
camera modules product line for convenient search and comparison by
sensors and camera modules features of the list.- [Camera sensor module, USB camera module]
- [Understanding imaging of camera module]
- [FOV (Angular Field of View)]
- [Global shutter vs Rolling shutter]
Camera
Modules List: Camera sensor module, USB camera module
Camera Sensor Module Guideline introduces
IADIY's image sensor modules, camera sensor modules and USB camera
modules product line for convenient search and comparison by sensors
and camera modules features of the list. You can open the guideline
accordions to review the list and related image sensor module, camera
module and USB camera module introduction and explanation.More camera modules and camera sensor modules with different camera lens module for optical requirements and image sensor module options are available additionally to the standard types. We also support the custom made camera modules, image sensor module and laser sensors as your requirements. Please send your requirements to us or leave the measage in comment below. We'll reply to you soon!
Welcome to visit our camera modules online store: https://www.iadiy.com/camera-module
Understanding
imaging of camera module
Camera
imaging refers to the process of capturing and creating images using a
camera. It involves the use of various components and technologies to
capture light and convert it into a digital or analog representation of
a scene.
The basic components of a camera imaging system typically include:
1. Lens: The lens captures light from the scene and
focuses it onto the camera's image sensor or film. Lenses play a
critical role in determining the field of view, focal length, aperture,
and image quality.
2. Image Sensor or Film: The image sensor (in digital
cameras) or film (in traditional film cameras) receives the focused
light and records the image. Image sensors convert light into
electrical signals, while film captures light on a photosensitive
emulsion.
3. Shutter: The shutter controls the duration of light
exposure to the image sensor or film. It opens and closes to allow
light to reach the sensor or film, determining the exposure time.
4. Image Processing: In digital cameras, image processing
algorithms are applied to the raw sensor data to optimize image
quality, adjust colors, reduce noise, and enhance details. This
processing may happen in-camera or during post-processing on a computer.
5. Storage: The captured image data is stored in digital
cameras on memory cards, while in film cameras, the image is recorded
directly onto the film.
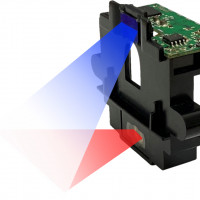
FOV
(Angular Field of View)
AFOV
stands for "Angular Field of View," which refers to the extent of the
observable scene that a camera can capture. It represents the angle,
measured in degrees, between the two extreme rays of the field of view
(FOV) from the camera's lens.
The FOV of a camera module depends on various factors, including the
focal length of the lens and the size of the camera's image sensor. A
wider focal length or a smaller image sensor size generally results in
a larger AFOV, while a narrower focal length or a larger sensor size
leads to a smaller AFOV.
To calculate the AFOV of a camera, you can use the following formula:
AFOV = 2 * arctan (D / (2 * F))
AFOV is the Angular Field of View in degrees.
D is the diagonal dimension of the camera's image sensor.
F is the focal length of the camera lens.
Global
shutter vs Rolling shutter
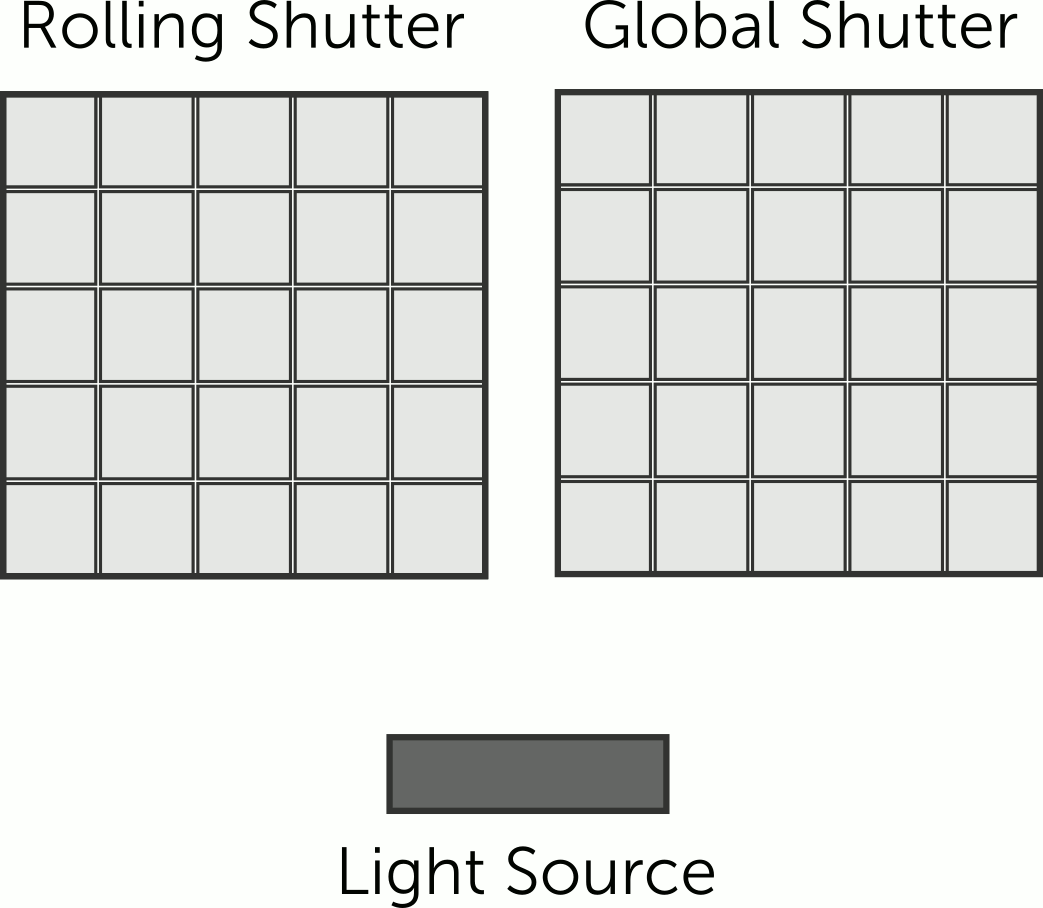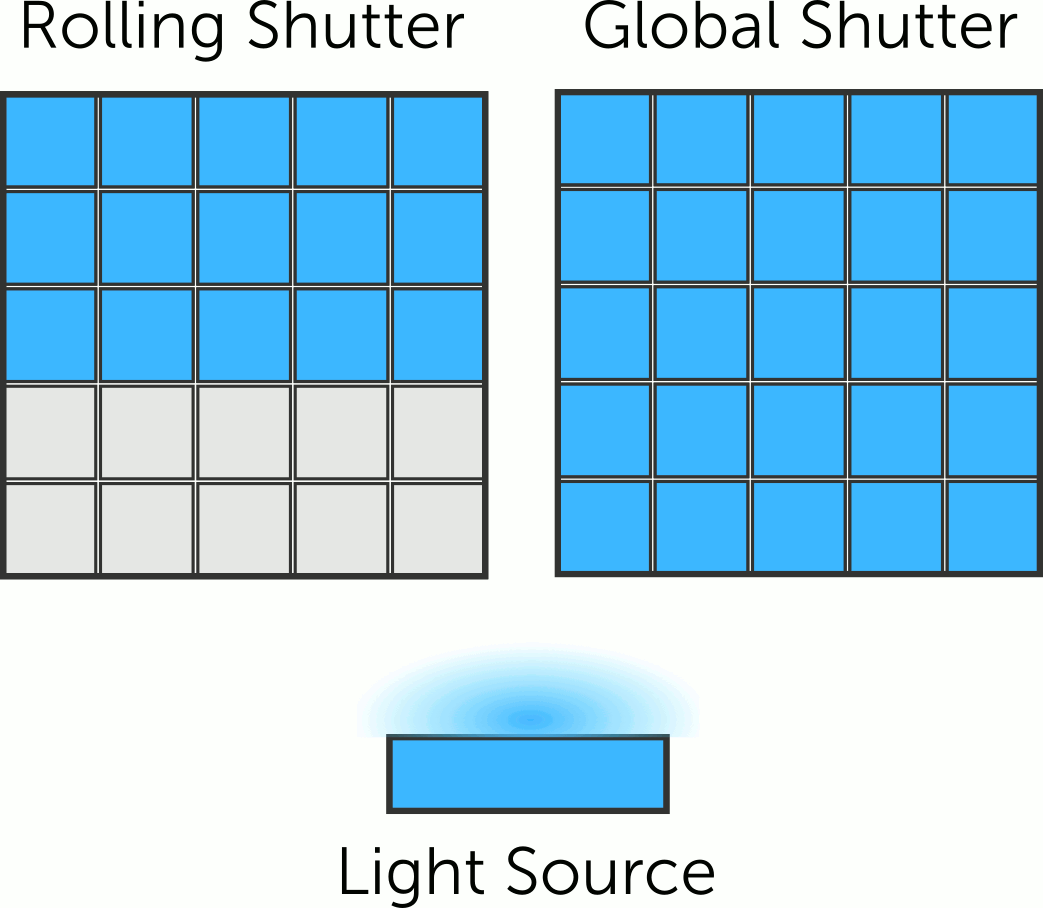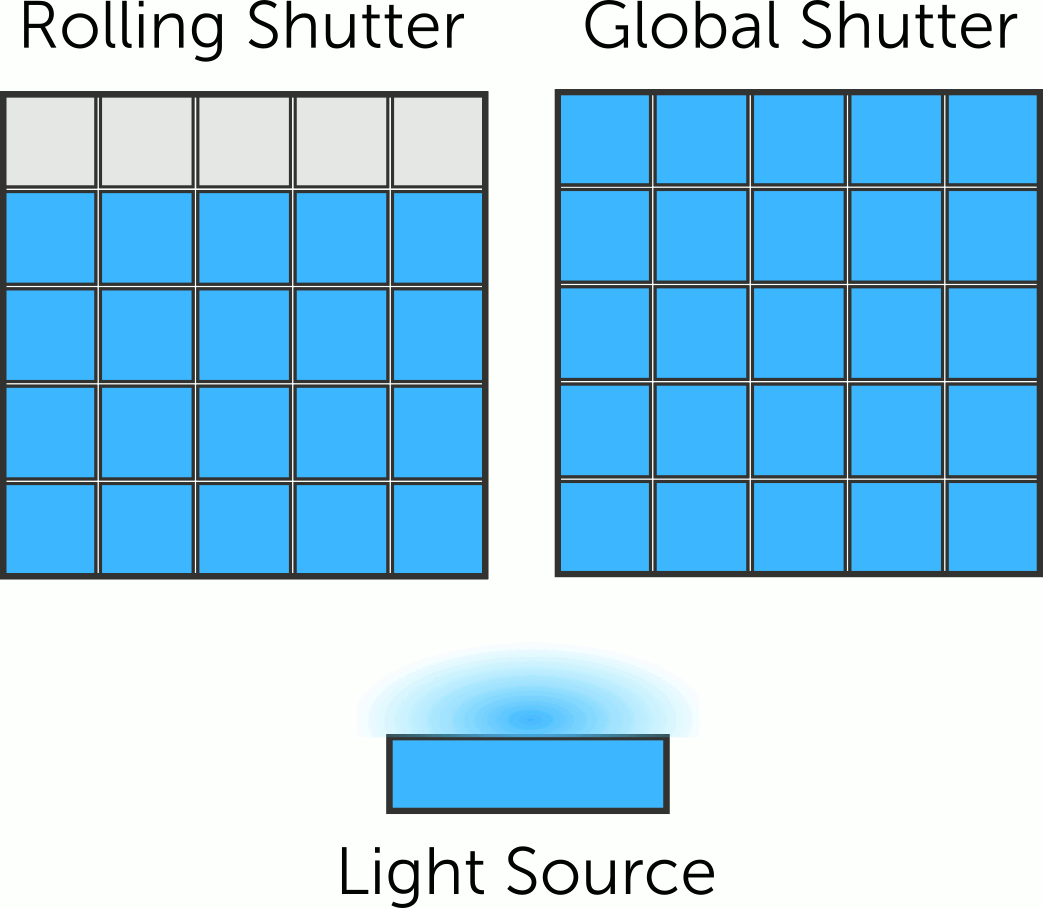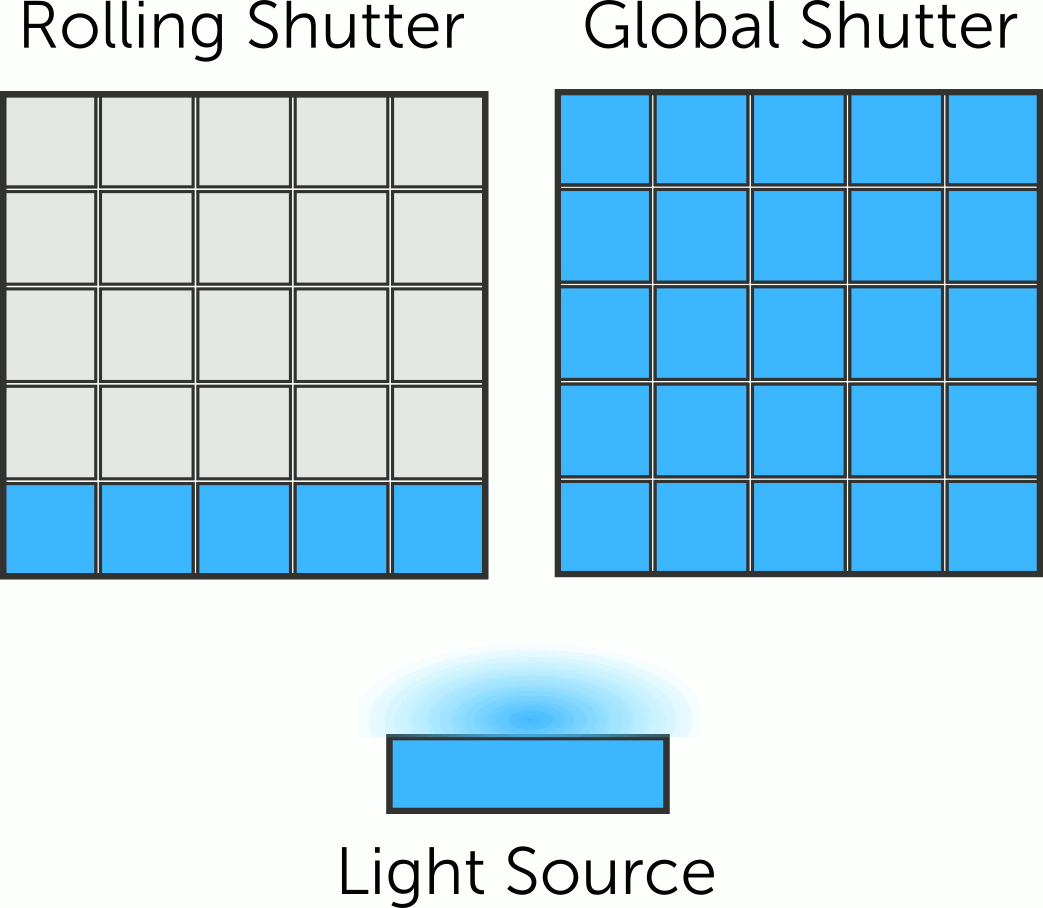 Rolling shutter
cameras capture the scene line by line, from top to bottom, causing a
time difference between top and bottom parts. Motion or camera movement
results in the distortion known as the rolling shutter effect.
Rolling shutter
cameras capture the scene line by line, from top to bottom, causing a
time difference between top and bottom parts. Motion or camera movement
results in the distortion known as the rolling shutter effect.
On the other hand, global shutter camera is
designated to capture an image by simultaneously exposing all the
pixels in its image sensor to light for a brief period of time. Unlike
a rolling shutter camera, which scans the image sensor row by row, a
global shutter camera captures the entire image instantaneously.
UVC protocol
The
UVC protocol, also known as USB Video Class, is a standard protocol
that defines how video streaming devices, such as webcams or digital
cameras, can communicate with computers over a USB connection. It
allows these devices to be easily recognized and used by various
operating systems without the need for additional drivers or software
installations.
Plug-and-Play: UVC is a plug-and-play protocol, meaning that when a
UVC-compliant device is connected to a computer via USB, the operating
system automatically detects and configures the device without
requiring manual driver installation. This makes it convenient for
users as they can simply connect the UVC device, and it will be ready
to use.
Cross-Platform Compatibility: UVC is designed to work across different
operating systems, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and Android. This
compatibility ensures that UVC-compliant devices can be used with
various devices and platforms seamlessly.
Video Streaming and Control: The UVC protocol defines the necessary
commands and data formats for video streaming and control functions. It
allows the video data captured by the device to be transferred over USB
and decoded by the receiving software on the computer. It also enables
control of parameters such as resolution, frame rate, exposure, and
focus settings.
Device Enumeration: UVC provides a standardized way for the computer to
enumerate and identify connected UVC devices. It allows the operating
system to recognize the device's capabilities and features, making it
easier for software applications to interact with the device.
USB Compliance: UVC operates within the USB framework and adheres to
USB specifications. It leverages the capabilities provided by USB, such
as data transfer rates, power management, and device configuration.
Application Support: UVC is widely supported by various software
applications, including video conferencing software, video recording
software, and video streaming platforms. This broad support ensures
that UVC-compliant devices can be used with a wide range of
applications without compatibility issues.





































Leave a Comment